Wounds Will Heal Faster Now: Nanotechnological Solution Produced from Marigold Flower with Green Synthesis
Yapılış Tarihi | 29 March 2024, Friday
This significant study was published in the first issue of 2024 of the International Wound Journal, a journal recognized internationally. The researchers emphasize the need to evaluate the effects of these nanoparticles on wound models created in experimental animals, and they continue their work in this field.
With the increase in chronic diseases worldwide, the need for innovative solutions in the field of wound healing is also increasing. In recent years, the number of studies aimed at designing nanomaterials with different properties for the healing of chronic wounds, which are one of the complications of diabetes, is increasing. Especially metal-based nanomaterials are attracting great interest in this field. Scientists from Burdur Mehmet Akif Ersoy University offer an effective solution for the healing of wounds that occur in chronic diseases such as diabetes, using zinc oxide nanoparticles produced by the "green synthesis" method, which is an environmentally friendly approach.
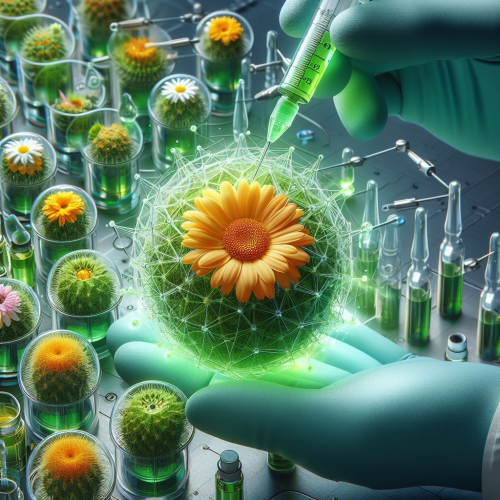
This innovative study has demonstrated the wound healing effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using calendula flower plant extract on fibroblast cells under laboratory conditions. In the study, researchers also emphasized that the synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles have antioxidant properties and this will also contribute positively to wound healing. The fact that these nanoparticles are effective quickly in wound models and are environmentally friendly makes the study even more important.
Green Nanotechnological Innovation: From Nature to Wound Healing
While this study provides a promising example of the integration of environmentally friendly approaches into medical applications, it is also a step for effective wound healing. This innovative research, as a strong example of the harmonious coexistence of nature and nanotechnology, is a candidate to play an important role in the health sector in the future.
This important study was included in the first issue of 2024 of the International Wound Journal, a recognized journal internationally. The researchers emphasize that the effects of these nanoparticles on wound models created in experimental animals should also be evaluated and they continue their work in this field.